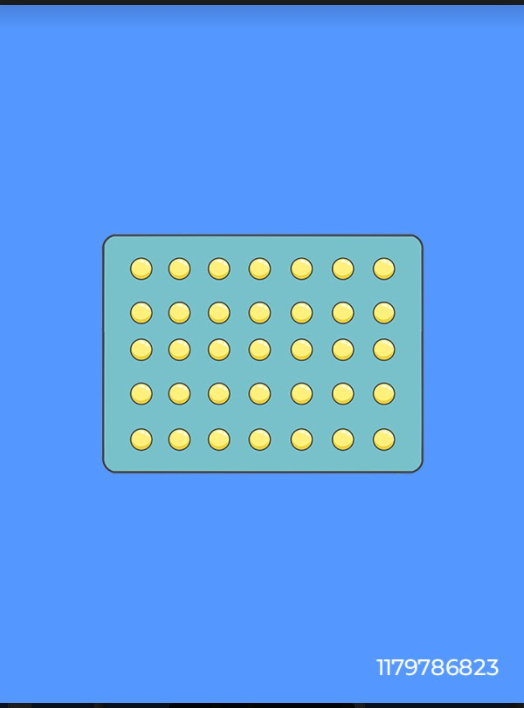
Progestin-only Contraceptive Pills (POPs)
Hormonal Method
Progestin-only Contraceptive Pills are also known as “the mini-pill” and only contain one hormone – progestin, in a smaller dose (typically 10% – 50%) less than that used in the combined pill.
How it works
The pill works by preventing the release of eggs from ovaries and thickening the cervical mucus, therefore preventing the sperm from meeting an egg.
Common Types of POPs
The common types of POPs contain 35 active pills in a single pack cycle.
Effectiveness
- When used consistently and correctly, POPs are 99% effective in preventing pregnancy
- Effectiveness depends on the user: For women who have monthly bleeding, risk of pregnancy is greatest if pills are taken late or missed completely.
- For greatest effectiveness, a woman must take one pill everyday.
Advantages
-
- Highly effective in protecting against pregnancy if used correctly and consistently.
- No delay in return to fertility after the pill is stopped.
- Safe for breastfeeding women and their babies since they do not affect milk production.


Limitations
- It is important to note that the pill must be taken daily at the same time each day whether or not a woman has sex that day.
- Does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Side Effects experienced by some users
- Changes in bleeding patterns such as spotting, bleeding in between menstrual periods, or lack of monthly periods
- Some women may experience nausea, mild headaches, dizziness, breast tenderness, weight change, mood changes, or weight changes
Juu life ni kujipanga!
Popular questions
You will get a small injection on your arm to numb you. This means you won’t feel pain at all during insertion. There will be a little pain or soreness as the wound heals for about a week.
Yes. A woman who has not had children generally can use an IUD, but she should understand that the IUD is more likely to come out because her uterus may be smaller than the uterus of a woman who has given birth.
Yes. If needed, ECPs can be taken again, even in the same cycle. A woman who needs ECPs often may want to consider a longer-acting and more effective family planning method
Yes. A woman who has not had children generally can use an IUD, but she should understand that the IUD is more likely to come out because her uterus may be smaller than the uterus of a woman who has given birth.
No. Most research finds no major changes in bleeding patterns after female sterilization. If a woman was using a hormonal method or IUD before sterilization, her bleeding pattern will return to the way it was before she used these methods



